Immunosuppression with Alemtuzumab (Campath)
Alemtuzumab is used for induction therapy in solid organ transplantation which is fundamental for long term graft survival. It is a potent immunosuppressant which lowers the body’s tendency to reject a newly transplanted organ. This drug has shown significant improvement in transplant patients lowering the risk of organ rejection and improving renal function. Campath is available free of cost through the campath access program for Liver India patients.
Genetic Testing for Tacrolimus and Azathioprine dosing
Post undergoing a transplant, patients require immunosuppression ( anti- rejection medications) to prevent their own immune system attacking the donor organ in their body. However, determining the appropriate dosage of these drugs has been a great challenge as these have toxic side effects at high doses and low doses might not provide enough immunosuppression. With the advent of genetic testing, it is now possible for us to predict the optimal doses of tacrolimus and azathioprine in order to achieve a safe dose while avoiding rejection.
Donor derived Cell free DNA (dd-cfDNA) to assess rejection
Early detection of organ rejection is key to preventing the loss of the transplanted organ. Genomic-based assay is a non-invasive and sensitive tool that measures donor-derived cell-free DNA (dd-cfDNA). It can be used to predict rejection, weeks and even months before biopsy testing. The dd-cfDNA can be detected in the recipient’s blood or urine and increased levels of these indicate acute rejection of the transplanted organ.
Sentinel Skin flap to monitor rejection
Reducing or eliminating any possibility of rejection is very important in the application of medicine. Our autoimmune response to foreign bodies is what causes rejection. Sentinel skin flap is a novel technique to monitor rejection by implanting a vascular donor derived skin flap as a graft on the recipient’s arm. The graft is examined visually to identify and monitor rejection of an internally transplanted solid organ or small bowel.
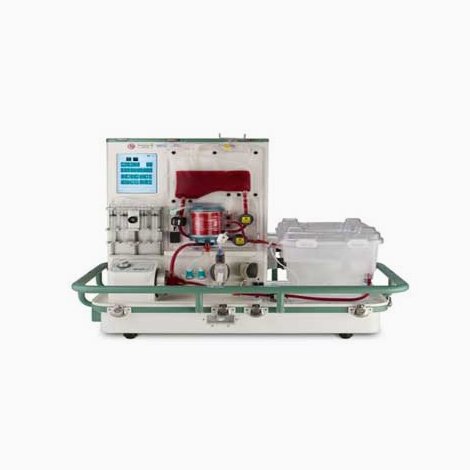
Hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion (HOPE)
HOPE has been associated with improved post-transplant outcomes, especially with grafts from donors with brain death or circulatory failure. This technique is based on the principle that hypothermia ( low temperature) slows down metabolism thus reducing oxygen requirements during the ischaemic period outside the human body. This machine allows storage of different organs and tissues being transported from the donor’s hospital to the recipient’s site.

Islet cell transplantation
A collection of cells present in your pancreas are known as Islets of Langerhans help your body in Insulin production. Islet cell transplantation is a particular experimental procedure by which we can manage type 1 diabetes. It is usually performed by collecting Islets from a deceased organ donor and injecting them to the healthy recipient.
The desired outcomes are:

Copyright © 2021. All rights reserved.